How to operate a drone is a question many ask, venturing into the exciting world of aerial technology. This guide provides a comprehensive overview, from understanding different drone types and pre-flight checks to mastering controls, planning flights, and capturing stunning aerial footage. We’ll cover safety regulations, maintenance, and troubleshooting, ensuring you’re equipped for responsible and successful drone operation.
Whether you’re a beginner eager to learn the basics or an intermediate pilot looking to refine your skills, this guide offers practical advice and detailed explanations to enhance your drone piloting journey. We explore various drone models, their unique operational characteristics, and essential safety procedures to ensure a safe and enjoyable experience.
Drone Types and Their Operation
Understanding the different types of drones and their unique operational characteristics is crucial for safe and effective operation. This section will explore the distinctions between multirotor, fixed-wing, and single-rotor drones, examining their control interfaces, specific models, and flight characteristics.
Multirotor, Fixed-Wing, and Single-Rotor Drone Operation
Multirotor drones, commonly known as quadcopters or octocopters, utilize multiple rotors for vertical takeoff and landing (VTOL) and exceptional maneuverability. Fixed-wing drones, resembling airplanes, require a runway for takeoff and landing, offering longer flight times and greater range but limited maneuverability. Single-rotor drones, or helicopters, combine VTOL capabilities with the directional control of a fixed-wing drone, providing a balance of versatility and flight time.
Drone Control Interfaces
Control interfaces vary significantly across drone models. Many utilize standard radio controllers with joysticks and buttons for flight control, while others incorporate smartphone or tablet apps for intuitive operation. Some advanced models offer features like autonomous flight modes and GPS waypoint navigation.
Specific Drone Models and Operational Features
The DJI Mavic 3 boasts advanced camera capabilities and obstacle avoidance, while the Autel EVO II offers impressive flight time and range. The Parrot Anafi is known for its compact size and portability. Each model possesses unique features impacting operational ease and capabilities.
Comparison of Flight Characteristics
| Drone Type | Maneuverability | Flight Time | Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| Multirotor | High | Moderate | Moderate |
| Fixed-wing | Low | High | High |
| Single-rotor | Medium | Medium-High | Medium |
Pre-Flight Checks and Procedures
A thorough pre-flight inspection is paramount for ensuring safe and successful drone operation. This involves checking various components and ensuring the drone is in optimal condition before takeoff.
Pre-Flight Inspection Steps
A comprehensive pre-flight check includes verifying propeller integrity, inspecting the drone’s body for damage, confirming proper GPS signal acquisition, testing the motors and control response, and examining the battery level and overall health. Visual inspection of the camera and gimbal is also crucial.
Pre-Flight Checklist
- Inspect propellers for damage
- Check drone body for damage
- Confirm GPS signal
- Test motors and control response
- Verify battery level and health
- Inspect camera and gimbal
Battery Health and Charging Procedures

Using a properly charged and healthy battery is essential. Always follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for charging procedures, avoiding overcharging or using damaged batteries. Monitor battery voltage and cycle count to ensure optimal performance and longevity. A sudden drop in voltage during flight is a clear indicator of a battery problem.
Potential Pre-Flight Issues and Resolutions
Common pre-flight issues include low battery levels, GPS signal loss, malfunctioning motors, or damaged propellers. Addressing these issues requires battery replacement, troubleshooting GPS connectivity, motor replacement or repair, and propeller replacement respectively. Always consult your drone’s manual for specific troubleshooting steps.
Understanding Drone Controls: How To Operate A Drone
Understanding the function of each control stick and button on your drone remote is fundamental to safe and effective operation. This section details the control inputs and their effect on the drone’s flight.
Drone Remote Control Functions

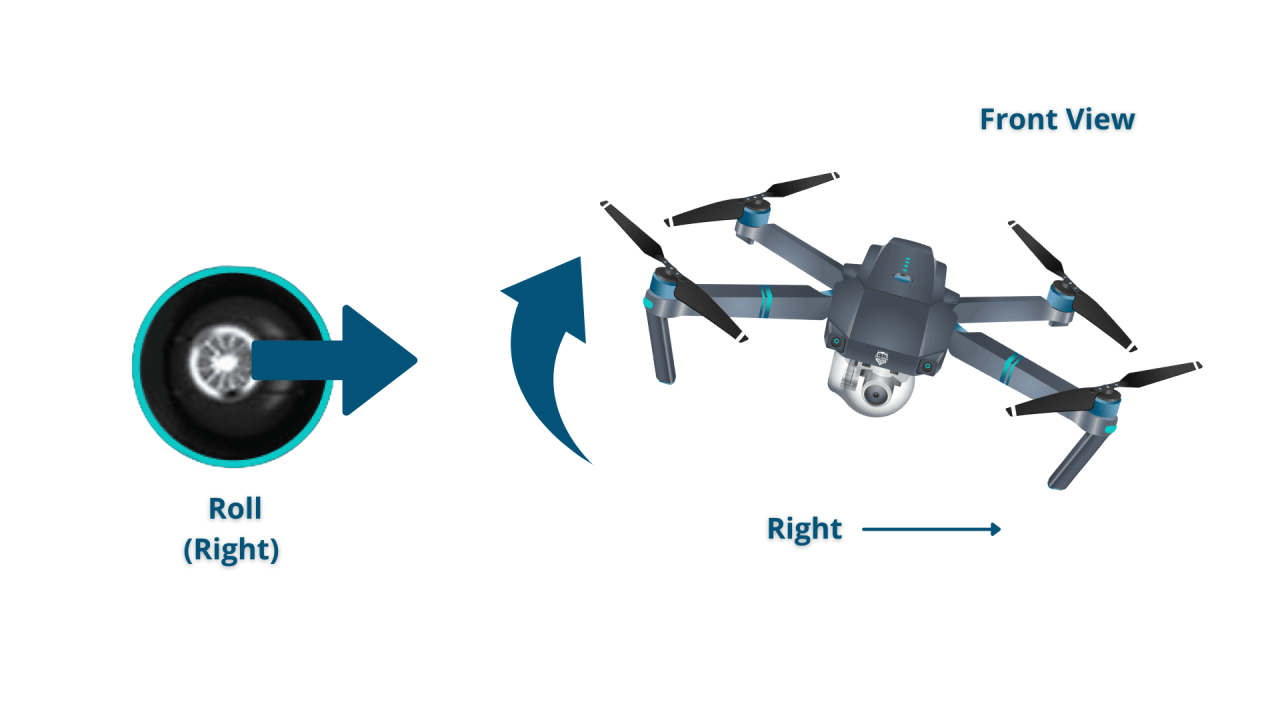
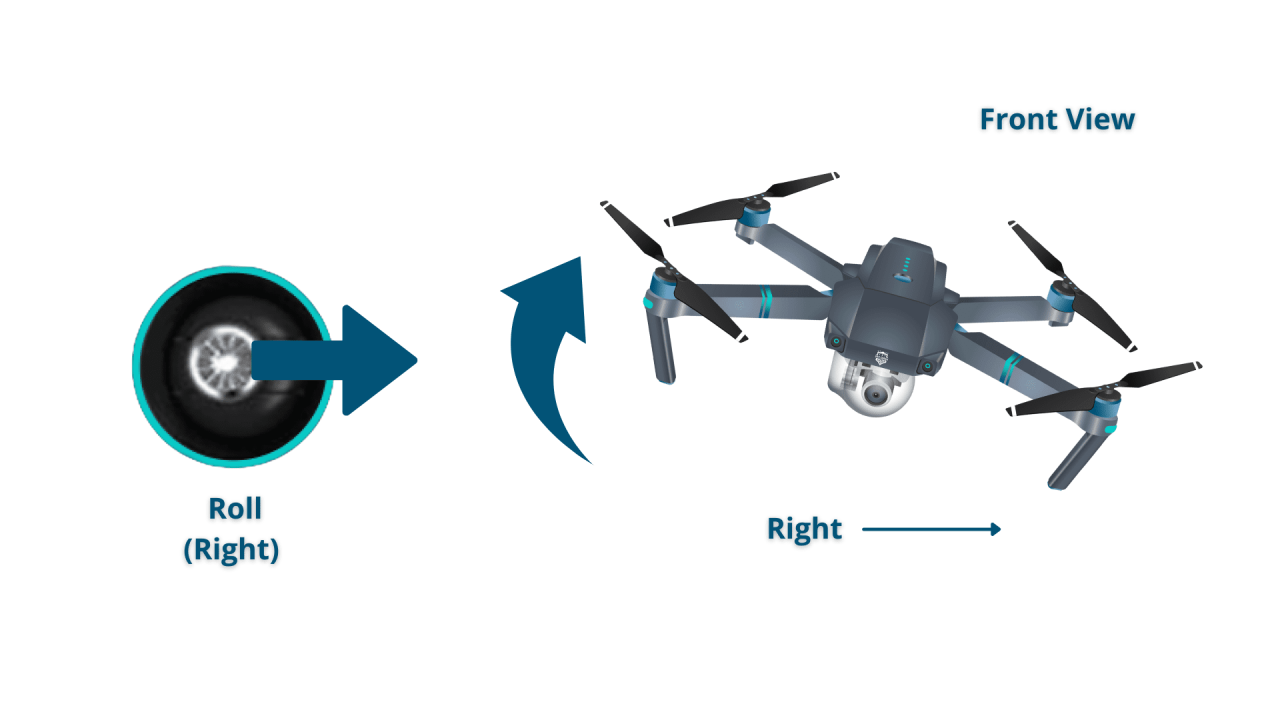
Typically, the left joystick controls altitude and yaw (rotation), while the right joystick manages roll (side-to-side tilt) and pitch (forward-backward tilt). Buttons on the remote are used for various functions, such as activating return-to-home, taking photos or videos, and adjusting flight modes.
Calibrating Drone Controls
Calibration ensures accurate control response. This typically involves placing the drone on a level surface, powering it on, and following the manufacturer’s instructions, often involving specific joystick movements or button combinations. Improper calibration can lead to unpredictable flight behavior.
Adjusting Drone Settings for Different Flight Conditions
Wind conditions significantly impact drone stability. In windy conditions, reducing speed and maintaining a steady hand on the controls is essential. Some drones allow adjusting flight parameters, such as responsiveness, to better handle wind gusts.
Visual Representation of Drone Control Inputs
- Left Joystick (Up): Increases altitude.
- Left Joystick (Down): Decreases altitude.
- Left Joystick (Left): Rotates counter-clockwise (yaw).
- Left Joystick (Right): Rotates clockwise (yaw).
- Right Joystick (Forward): Moves forward (pitch).
- Right Joystick (Backward): Moves backward (pitch).
- Right Joystick (Left): Moves left (roll).
- Right Joystick (Right): Moves right (roll).
Taking Off, Flying, and Landing
Safe takeoff, flight, and landing procedures are critical for preventing accidents. This section Artikels the proper techniques and emergency procedures.
Safe Takeoff and Landing Techniques
Begin by ensuring the area is clear of obstacles and people. For takeoff, gently increase throttle until the drone lifts off vertically. Maintain a steady hand on the controls during flight. For landing, slowly decrease throttle until the drone gently touches down. Always maintain visual contact with the drone.
Maintaining Stable Flight
Smooth and controlled movements are key to stable flight. Avoid abrupt changes in direction or altitude. Practice flying in calm conditions before attempting more challenging maneuvers.
Emergency Procedures
In case of control loss or malfunction, immediately activate the return-to-home (RTH) function, if available. If RTH fails, attempt to regain control using smooth, controlled inputs. If the drone is unresponsive, prioritize safety and let it land where it may, avoiding populated areas if possible.
Flowchart for Safe Drone Flight
A flowchart would visually represent the steps: Pre-flight checks -> Takeoff -> Flight (maintaining stability) -> Landing -> Post-flight checks. Each step would have specific actions and decision points (e.g., wind conditions, malfunction detection).
Navigation and Flight Planning
Effective navigation and flight planning are essential for safe and efficient drone operation, especially in complex environments or for extended flights.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating the airspace requires a good grasp of the fundamentals, and for a comprehensive guide, I recommend checking out this excellent resource on how to operate a drone which covers everything from basic maneuvers to advanced techniques. Ultimately, safe and effective drone operation hinges on proper training and understanding of the regulations.
Using GPS and Navigation Systems
Most modern drones utilize GPS for positioning and navigation. This allows for features like return-to-home and waypoint navigation, where pre-programmed flight paths can be followed autonomously. Some drones offer advanced features like obstacle avoidance using GPS data and sensors.
Flight Path Programming
Many drone apps allow for programming waypoints, creating complex flight paths. This involves selecting points on a map and setting parameters like altitude and speed for each waypoint. Simpler drones might offer pre-set flight modes, such as circular flight or specific patterns.
Successfully piloting a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics, such as calibrating the drone and practicing in open spaces, is crucial before undertaking more complex maneuvers. For a comprehensive guide covering everything from pre-flight checks to advanced techniques, consult this excellent resource on how to operate a drone. Mastering these skills ensures safe and effective drone operation, ultimately leading to a more enjoyable and productive experience.
Airspace Regulations and Restrictions
Understanding airspace regulations is crucial. Restricted airspace includes airports, military bases, and other sensitive areas. Operating a drone in restricted airspace can result in legal penalties. Always check local regulations before flying.
Navigating a Challenging Flight Path
Consider a scenario involving a flight through a narrow canyon. Careful pre-flight planning is crucial, including waypoints for precise navigation and consideration of wind conditions. Real-time adjustments might be needed to avoid obstacles and maintain stability.
Drone Photography and Videography
High-quality aerial photography and videography require understanding camera settings and composition techniques. This section provides guidance on achieving optimal image quality.
Adjusting Camera Settings
Camera settings like ISO, shutter speed, and aperture impact image quality. Higher ISO values increase sensitivity in low light but can introduce noise. Shutter speed affects motion blur; a faster shutter speed freezes motion, while a slower speed creates motion blur. Aperture controls depth of field.
Capturing High-Quality Aerial Media
Factors influencing quality include lighting, stability, and composition. Shooting during the golden hour (sunrise and sunset) provides soft, warm light. Using a gimbal helps stabilize the camera, reducing shake. Proper framing and composition enhance visual appeal.
Camera Angles and Visual Storytelling
Different angles create different effects. High-angle shots provide a broader perspective, while low-angle shots emphasize scale and drama. Choosing the right angle helps tell a story through the imagery.
Composing Shots for Aesthetically Pleasing Imagery
Composition principles like the rule of thirds and leading lines apply to aerial photography. Placing the subject off-center (rule of thirds) often creates a more dynamic image. Using leading lines guides the viewer’s eye through the scene.
Drone Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance is vital for extending the lifespan of your drone and preventing malfunctions. This section Artikels a maintenance schedule and common troubleshooting steps.
Regular Maintenance Schedule
A regular schedule should include inspecting propellers for damage, cleaning the drone body, lubricating moving parts (as per manufacturer recommendations), checking and cleaning the camera lens, and storing the drone in a cool, dry place. Battery maintenance, including proper charging and storage, is also crucial.
Cleaning and Storage
Use a soft cloth to gently wipe down the drone body, avoiding harsh chemicals. Store the drone in a protective case away from dust, moisture, and extreme temperatures. Batteries should be stored separately, at a recommended storage charge level.
Common Drone Malfunctions and Troubleshooting
Common issues include motor failures, GPS signal loss, camera malfunctions, and battery problems. Troubleshooting involves checking for physical damage, inspecting connections, calibrating sensors, and replacing faulty components. Consult your drone’s manual for specific troubleshooting guidance.
Troubleshooting Guide, How to operate a drone
| Problem | Possible Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Drone won’t power on | Low battery, faulty battery, power switch issue | Charge battery, replace battery, check power switch |
| GPS signal lost | Obstructed signal, faulty GPS module | Move to open area, contact manufacturer for repair |
| Motor malfunction | Faulty motor, loose connection | Inspect motor, check connections, replace motor |
Safety Regulations and Legal Considerations
Adhering to local drone regulations is crucial for safe and legal drone operation. This section highlights the importance of understanding and respecting these regulations.
Importance of Adhering to Local Regulations
Ignoring regulations can lead to fines, legal action, and potential harm. Regulations vary by location, so it’s essential to research and understand the specific rules in your area before flying.
Legal Implications of Airspace Violations
Flying in restricted airspace, such as near airports or military bases, is illegal and can result in severe penalties, including hefty fines and potential criminal charges.
Situations Where Drone Operation Might Be Restricted
Drone operation is often restricted near airports, stadiums, emergency scenes, and areas with high population density. Weather conditions, such as strong winds or heavy rain, can also necessitate grounding the drone.
Essential Safety Guidelines
- Always maintain visual line of sight with your drone.
- Never fly near airports or other restricted airspace.
- Avoid flying over crowds or populated areas.
- Respect privacy and avoid filming people without their consent.
- Be aware of weather conditions and avoid flying in adverse weather.
Mastering drone operation involves a blend of theoretical knowledge and practical experience. This guide has equipped you with the foundational skills and safety awareness necessary to confidently navigate the skies. Remember, continuous learning and adherence to regulations are crucial for responsible and enjoyable drone piloting. Safe and happy flying!
Question & Answer Hub
What is the minimum age to operate a drone legally?
Legal age requirements vary by location and drone classification. Check your local regulations for specific age limits.
How often should I calibrate my drone’s controls?
Calibration is typically recommended before each flight session, or if you notice erratic flight behavior.
What should I do if my drone loses signal?
Most drones have a return-to-home (RTH) function. Activate this immediately. If unavailable, attempt to regain signal, then perform a controlled emergency landing.
Can I fly my drone in rain or strong winds?
No. Operating a drone in adverse weather conditions is dangerous and can damage the drone. Wait for favorable weather.
How do I register my drone?
Registration requirements vary by country and drone weight. Check your local aviation authority’s website for details.